Salesforce Agentforce 360: The Future of the AI-Driven Enterprise
Salesforce Agentforce 360 marks a major leap forward in the evolution of enterprise AI, bringing autonomous, reasoning-driven digital agents directly into the core of the Salesforce ecosystem. Built on Data Cloud, Einstein 2, and the platform’s extensive automation capabilities, Agentforce 360 enables businesses to deploy AI workers that can understand context, execute multi-step tasks, and collaborate seamlessly with human teams. With built-in observability, strong governance controls, and preconfigured agents for sales, service, marketing, and industry clouds, Agentforce 360 transforms how organizations operate—shifting from reactive workflows to proactive, intelligent automation at scale. It represents Salesforce’s bold vision for the AI-driven enterprise, where data, automation, and generative intelligence combine to deliver unprecedented efficiency and customer value.
Over the past decade, Salesforce has transformed from a CRM pioneer into one of the world’s most influential cloud ecosystems. But as businesses race into an AI-first era, expectations for automation, personalization, and operational efficiency have risen dramatically. Traditional workflows, even when optimized, cannot keep pace with the modern enterprise’s need for real-time decision-making and deeply intelligent operations.
This led to the creation of Agentforce 360, Salesforce’s next-generation AI agent platform that unifies data, automation, and generative intelligence into a single, continuously learning system.
Unveiled at Dreamforce and expanded with the Winter ’26 release, Agentforce 360 represents Salesforce’s bold step into the world of autonomous enterprise AI, pushing beyond chatbots or isolated automation flows. Instead, it introduces dynamic, reasoning-capable AI agents that can understand context, take actions, and deliver business results across every Salesforce cloud.
This article explores what Agentforce 360 is, how it works, and why it is becoming foundational for the emerging “agentic enterprise.”
What Is Agentforce 360?
At its core, Agentforce 360 is a system for creating, orchestrating, and monitoring autonomous AI agents within the Salesforce ecosystem. These agents can perform tasks ranging from answering customer inquiries to executing internal processes such as lead enrichment, order processing, case triage, and compliance validation.
Unlike earlier AI features (Einstein GPT, Einstein Bots, or static automation), Agentforce 360 agents are:
Contextual — they interpret data and past actions before deciding what to do.
Multi-step — they carry out sequences of actions, not just single responses.
Connected — they operate across Salesforce Data Cloud, CRM, MuleSoft, Tableau, and third-party apps.
Observable — admins can see the reasoning path, steps, and decisions each agent takes.
Secure and governed — guardrails, permissions, and data policies are built-in.
In simple terms: Agentforce 360 gives companies digital workers that can think, act, and adapt.
The Architecture Behind Agentforce 360
Salesforce built Agentforce 360 on top of three major pillars of its modern ecosystem:
1. Data 360 — Unified, Governed Enterprise Data
AI agents are only as good as the data they rely on.
Data 360 combines:
Salesforce CRM
Marketing and Commerce data
External system data (via MuleSoft)
Real-time streaming data
Historical customer models
This unified layer ensures that Agentforce agents operate using clean, contextual, permissioned information. The recent acquisition of Informatica only strengthens this foundation with enterprise-grade:
Data governance
Metadata management
Data lineage tracking
Master Data Management
Data cataloging
2. Einstein 2 and LLM-Based Reasoning
Agentforce uses Einstein 2, Salesforce’s own LLM family, tuned specifically for CRM and enterprise operations. It supports:
Natural language understanding
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) using Data Cloud
Action reasoning and tool-calling
Step-by-step task execution
Error and exception handling
Einstein 2 ensures that Agentforce agents can propose actions such as:
“This case is high priority due to SLA terms. Reassigning to Tier 2, sending escalation email, and updating status.”
And then execute these actions automatically.
3. Flow, Apex, and Automation Tools
Agents integrate deeply with Salesforce automation layers:
Flows (the execution engine for multi-step logic)
Apex actions
Invocable actions
OmniStudio for industry clouds
MuleSoft RPA and API flows
This means that an AI agent can:
Trigger a record update
Call an Apex class
Start an RPA bot
Query external data
Orchestrate a full business workflow
No other CRM vendor offers this level of integration between AI and operational systems.
Key Capabilities of Agentforce 360
1. Autonomous Action Execution
Agents can act on behalf of employees across departments. Examples:
Sales: qualify leads, update opportunities, generate follow-ups
Service: resolve cases, escalate issues, or book appointments
Marketing: create campaigns, segment audiences, analyze performance
Operations: process documents, validate inventory, approve workflows
They learn from previous actions and adjust accordingly.
2. Agentforce Observability
One of the biggest concerns with AI is the “black box” problem:
Why did the AI do that?
Salesforce addresses this with Agentforce Observability, a dashboard that shows:
Each reasoning step (“thought process”)
Tools the agent called
Data sources used
Errors or exceptions
Guardrails triggered
Suggested improvements
This gives admins and developers transparency and control, making AI deployment safer and more auditable.
3. Domain-Specific Agents for Every Cloud
Salesforce includes prebuilt agents such as:
Sales Agent – pipeline updates, deal summaries, customer outreach
Service Agent – case triage, resolution drafting, SLA monitoring
Commerce Agent – product recommendations, order management
Marketing Agent – content generation, campaign optimization
Industry agents (Healthcare, Financial Services, Utilities, Public Sector, etc.)
These out-of-the-box agents drastically reduce implementation cost and time.
4. Agent Studio
Admins can build custom agents without code:
Define the agent’s role
Choose data sources
Pick allowed actions
Add guardrails
Configure business rules
Simulate agent behavior
For developers, Agent Studio exposes deeper options using:
Apex
Flow Orchestration
Transport APIs
Custom Tooling APIs
Agentforce is not just a chatbot builder — it is a full AI worker creation platform.
Use Cases Across the Enterprise
Where Agentforce 360 shines is its ability to improve efficiency, accuracy, and velocity across every business function.
1. Customer Support Modernization
Before Agentforce:
Agents manually triage cases, read long histories, escalate issues, and draft responses.
This is time-consuming and inconsistent.
With Agentforce:
Reads entire case history
Detects tone, sentiment, urgency, and SLA
Suggests resolution or takes actions directly
Escalates only when needed
Generates customer-ready responses
Updates the case automatically
This reduces handling time by up to 40-60%.
2. Sales Acceleration
Sales reps spend most of their time on admin work instead of actual selling.
Agentforce can:
Auto-update opportunities
Summarize meeting notes
Generate outreach emails
Validate pricing and quoting
Analyze pipeline health
Alert reps about stalled deals
This turns Salesforce into a proactive co-seller, not just a CRM.
3. Marketing Personalization at Scale
Marketing teams can use Agentforce to:
Build audience segments dynamically
Create high-quality content
Optimize email journeys
Analyze campaign performance
Suggest improvements
And because it’s tied into Data Cloud, segmentation becomes real-time instead of static.
4. Operations & Workflow Automation
Complex operations — such as loan processing, insurance underwriting, or compliance — rely on multi-step workflows.
Agentforce can handle:
Document analysis
Eligibility validation
Data enrichment
Multi-system calls
Exception handling
Human approvals when required
This is especially valuable for enterprises with multiple legacy systems.
Why Agentforce 360 Matters for the Future
1. It solves the AI adoption challenge
Many companies struggle to implement AI because they lack:
Clean data
Integration
Governance
Automation structure
Agentforce solves all four.
2. It brings AI into business operations, not just around them
Instead of having a chatbot “suggest” actions, agents do the work.
3. It sets a new standard for audited, safe enterprise AI
Observability and compliance controls are unmatched in the industry.
4. It positions Salesforce as the leader of the “agentic enterprise”
Just as Salesforce defined the modern CRM, it is now defining the next evolution:
AI that manages the CRM for you.
Challenges and Considerations
Agentforce 360 is powerful — but like any AI platform, it requires careful planning.
Agents must operate on clean, well-structured, permissioned data.
Role-based access, guardrails, and action controls must be configured.
Just because an agent can automate a workflow doesn’t mean it should without review.
AI agents consume API and generative compute resources — costing must be monitored.
Conclusion: The Dawn of the AI-Driven Enterprise
Salesforce Agentforce 360 is more than a new product — it is the foundation for a new era of enterprise operations where AI agents work alongside employees to streamline processes, improve customer outcomes, and accelerate revenue.
Its combination of:
Deep CRM integration
Unified enterprise data
Generative reasoning
Transparent observability
Strong governance
makes it one of the most advanced and practical enterprise AI platforms available today.
As businesses move toward intelligent automation, Agentforce 360 will play a defining role in shaping how modern organizations operate — with AI at the core, not the periphery.
Top Developer-Focused Enhancements in Winter ’26
1. Trusted Mode for LWC / Browser API Access
A new “Trusted Mode” lets you relax some of the sandbox constraints imposed by Lightning Web Security / Locker, allowing direct access to
window,document, and full DOM manipulation (including Salesforce-managed components).You’ll need to explicitly enable it and whitelist static resources to run in trusted mode.
Caveat: As of mid-Sept, Salesforce had temporarily removed Trusted Mode from the official release notes, indicating it might still be refined.
2. Better Local Development: Single-Component Local Dev
The LWC local development environment is enhanced: you can now run single components in localhost mode, supporting
@salesforce/*modules, public Lightning Data Service wire adapters, and Apex calls.This speeds up iterative dev cycles without needing to spin up full pages or apps.
3. ApexDoc becomes native / integrated
The open-source ApexDoc (documentation generator for Apex classes & triggers) is becoming a first-class capability in Winter ’26.
This suggests better alignment of code comments, metadata, and possibly auto-generated human-readable Apex documentation.
4. Stricter Permission Checks for Apex Invoked in Flows
Any Apex classes used in Flows will now enforce permission checks based on the current user’s context (rather than implicitly inheriting the permission context).
If your existing flows call Apex, you must ensure the calling users have necessary permissions.
5. Flow + Automation Upgrades
Compare Flow Versions: view and diff changes between versions of a Flow.
New Debug Experience for Screen Flows: side-by-side canvas + debug detail, more interactive debugging.
AI-powered Decision Elements: you can now use unstructured data to derive decisions using AI inside Flows.
Immediate access to Created Records: you can reference output fields of newly created records directly, without needing a Get Records step.
Enhanced Resource Menu Filtering: Flow’s UI will now show only relevant variables, resources, nested fields, etc., based on context — reduces clutter.
6. Lightning Out 2.0 Enhancements & External App Integration
You can embed Salesforce UI capabilities externally via Lightning Out 2.0 more robustly (Professional, Enterprise, Performance, Unlimited, Developer editions).
Better support for component reuse in external apps (beyond just LWC in standard pages).
7. Experience / LWR Sites Upgrades
Enhanced LWR (Lightning Web Runtime) site features: expression-based visibility, component-specific CSS styles, improved CMS search, and Data Cloud integration for site audience data.
Upgrading an existing LWR site changes metadata types (ExperienceBundle → DigitalExperienceBundle / DigitalExperienceConfig) — backup first. 8. Platform / Data / Integration Enhancements
Tools for smoother Hyperforce data migration and automation — helping orgs move to the public cloud infrastructure more easily.
ITechCloud notes “Einstein for Developers (pilot)” — AI assistance inside VS Code / Code Builder for generating test classes, explaining code, writing snippets.
8. Rich Text for Case Comments
Rich Text Comments become generally available in this release. Case comments can now support formatting (bold, italics, lists), inline images, and media.
In Setup → Support Settings, look for the option “Rich Text for Case Description” and enable it.
Salesforce’s brand-new Flow Approval Processes
Salesforce has revolutionized the way organizations manage approvals with the introduction of Flow Approval Processes—a powerful new feature that brings flexibility, automation, and visual orchestration to the forefront of business workflows. Replacing traditional approval mechanisms, this declarative, no-code solution enables admins to build multi-step, multi-approver processes using Flow Builder. In this article, we explore how Flow Approval Processes work, what makes them different from classic approvals, and how to get started with this game-changing tool in the Spring and Summer ’25 releases.
Introduced in the Spring ’25 and expanded in Summer ’25 releases. This feature marks a major evolution of classic Approval Processes, now fully integrated within the Flow Orchestration framework.
What Are Flow Approval Processes?
Flow Approval Processes are a new Flow Approval Orchestration feature from Salesforce Spring ’25, replacing classic Approval Processes with fully declarative orchestration workflows—without consuming automation credits. You can build them as either:
Record‑Triggered Approval Orchestrations (auto-launch on record create/update)
Autolaunched Approval Orchestrations (triggered from other Flows or UI elements)
They allow multi-stage, multi-step approval workflows using screen flows for interactive steps and background steps for automation.
Key Benefits & Why You Should Migrate
Visual orchestration: Design approval workflows in Flow Builder, with clear stages, steps, and logic.
Multi-level approvals: Support sequential or parallel multi-user approvals, even across external stakeholders.
Conditional routing via Decisions & Evaluation Flows for approval logic paths.
Record locking, custom notifications, email reply approvals (“Approve” or “Reject”).
New central Lightning App titled "Approvals" offering visibility into Approval Submissions, Work Items, and audit tracking.
Migrates away from legacy Approval Processes with better flexibility and future-proofing.
Plus, they’re free to use if you have eligibility for legacy Approval Processes: orchestrations don’t consume automation entitlements.
Anatomy of a Flow Approval Orchestration
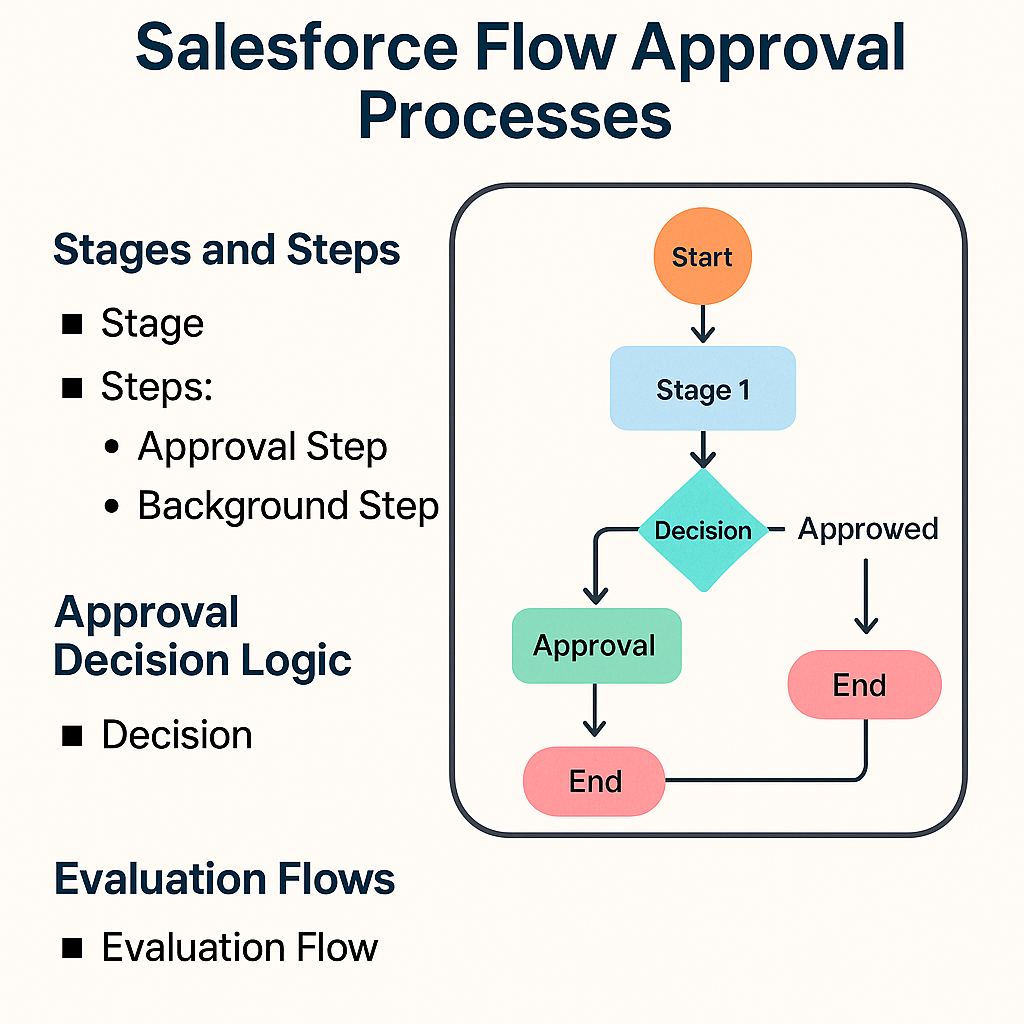
a) Stages and Steps
A Stage is a phase in the process.
Steps within a stage can be:
Approval Step: interactive, requires approver action via a screen flow.
Background Step: automatically runs an autolaunched Flow for tasks like record updates.
b) Approval Decision Logic
Each Approval Step outputs a variable approvalDecision (‘Approve’ or ‘Reject’). Use Decision elements to route logic based on this and other criteria.
c) Evaluation Flows
Use these to define when a stage completes, when steps should start, or when approval steps finish. They output the boolean variable isOrchestrationConditionMet to control orchestration flow
Building a Sample Approval Flow
Scenario: An Opportunity gets submitted for approval upon creation, routing to the owner’s manager. After approval, a task is created.
Step-by-Step:
Create the screen Flow (Evaluate Approval Requests template) for the interactive step. Define output variables
approvalDecision,approvalComments.Create an autolaunched Flow to update a custom field (e.g. Opportunity Approval_Status__c).
In Flow Builder:
Use Record‑Triggered Approval Orchestration type.
Stage 1:
Approval Step: assign manager; lock record, customize emails.
Background Step: update record/status/task creation.
Add Decision element to branch: Approved vs Rejected path.
Activate orchestration and add the Flow Orchestration Work Guide Lightning component to the Record Page so approvers see tasks in UI.
You’ll then see the process in action: approver’s Work Guide, record trace components, and audit via Approval Submission and Work Items list views.
What’s New in Summer ’25
Salesforce recently added enhancements:
Flow Approval Process creation wizard: Graphically set number of levels and recall paths, then generate an orchestration skeleton automatically.
Recall path support: Users can recall approval processes mid‑flow; now achievable entirely within Flow orchestration.
Visual improvements in Flow Builder: debug enhancements, time data types, better previews, etc.— making orchestration design more intuitive overall.
These orchestrations utilize new core Salesforce objects:
Approval Submission
Approval Submission Detail
Approval Work Item
Orchestration Run
A new Lightning “Approvals” app surfaces these objects for admins and users to monitor and manage audit trails.
Admins can also leverage custom Report Types on these objects for deeper reporting and dashboards.
Best Practices & Planning
Design Stages & Steps carefully: Use parallel steps where needed, lock records only once if parallel approvals occur.
Cover rejection paths explicitly: don’t assume consensus.
Use Evaluation Flows if decision logic exceeds simple checks.
Configure recall flows to support reversal mid-process.
Manage notifications smartly: keep org-wide approvals emails active; you can suppress individual flows if needed.
Test extensively: test edge cases like approver unavailability, timeouts, etc.
Limit versions: Flow versions capped at 50 per orchestration; manage versioning wisely.
Known Limitations
Autolaunched orchestrations can only be triggered via record‑triggered flows; not directly from buttons/UI via screen flows. Users workaround this using Apex invocable actions to start approval processes from custom buttons.
Manual approver selection during runtime is not supported yet—approvers must be predefined in step configuration.
Overall, Flow Approval Processes deliver flexibility but require planning to avoid pitfalls.
If your org still uses legacy approval processes, now is the time to plan a migration to flow-based orchestration.
Final Thoughts & Recommendations
Treat Flow Approval Processes as the future of automation in Salesforce — not just a successor to classic approvals, but a transformative tool that unifies logic, UI, and automation.
Begin by mapping existing business approval processes, then replicate in Flow Orchestration with proper stages, steps, and decision logic.
Leverage the built‑in wizard in Summer ’25 to quickly bootstrap approval flows.
Train users and admins on Work Guide usage, audit tracking, and recall operations.
Continuously test and monitor orchestration runs and error-handling outputs.
Resources & References
Detailed introduction and sample build: Salesforce Ben’s “Flow Approval Processes: Get Started Now”.
Salesforce Break blog article: “Supercharge Your Approvals with Salesforce Flow Approval Processes”.
CLD Partners architecture best practices: “Anatomy of a Flow Approval Process” guide.
Official Salesforce Help documentation (Flow Approval Process concepts & steps).
Conclusion
Flow Approval Processes are a game‑changing addition to Salesforce’s automation portfolio, offering modern, flexible orchestration capabilities that empower declarative admins to design complex approval workflows with precision and control. From multi‑user stages to conditional logic, recall, and audit tracking, this new tool belongs in every org’s automation strategy.
(The article including images as shown in this summary reflects product features available in Spring ’25 and Summer ’25 releases.)
Salesforce AgentForce: A New Technology for Creating AI Agents
Salesforce AgentForce: A New Technology for Creating AI Agents
At the end of last year, Salesforce introduced AgentForce, a groundbreaking technology for developing AI agents. This innovation has ignited a discourse regarding its potential impact on engineering challenges and the role of engineers in the future.
The purpose of this article is to provide an in-depth analysis of AgentForce. I will also share my perspective on whether this technology warrants a reevaluation of our approach to CRM system interactions or if it should be viewed as a mere extension of the global trend in artificial intelligence development.
What is AgentForce?
As outlined in Salesforce’s official press release, AgentForce is a groundbreaking and trustworthy solution that seamlessly integrates artificial intelligence into any workflow, poised to revolutionize the landscape of CRM systems. Furthermore, Salesforce has developed its own robust security framework and adheres to stringent standards for handling personal customer data, ensuring the utmost confidentiality and security of information processed by a large language model.
Several times I’ve encountered clients expressing concerns about how Salesforce can align with the global trend of implementing artificial intelligence. In October 2024, Salesforce exposed AgentForce, a comprehensive suite of modules designed to optimize workflows within Sales and Service clouds. This raises the question of whether AgentForce can enhance the productivity of sales and customer support agents. While this question may appear somewhat superficial and lacking in specificity, it is important to consider the potential benefits.
Throughout my extensive experience in various project roles, I have observed that the requirements for system development are rarely complete or well-defined. Instead, they often evolve through a process of clarification and refinement to meet the unique needs of each business. No process can be replicated exactly, even within the same industry, region, or direction.
Given this context, let us consider the implications of implementing artificial intelligence within a business. What can we anticipate?
Essential Component for Contemporary Contact Centers and Sales Platforms
In the modern contact center and sales environment, agents anticipate dedicating their time and attention to resolving specific client inquiries and crafting mutually beneficial offers. However, they do not typically engage in tasks such as searching for relevant information within the CRM system or considering the creation of correspondence to clients inviting events or presenting alternative products. AgentForce presents a significant opportunity to automate these repetitive tasks.
During the development of an agent for a one of the client, I identified numerous new opportunities.
Presently, it is feasible to implement a solution that, at the request of a manager, AI agent can display information in a user-friendly format, tailored to customer interests, thereby suggesting relevant products. This approach can be particularly effective in identifying customers who may be interested in or have access to services located near their current location. Subsequently, an email can be prepared containing a comprehensive list of products or services that align with these customer preferences. An email invitation for a distinct event, along with numerous other actions, can be prepared.
Configuring an AI agent to execute actions involves providing a detailed description of the task in plain language. This description specifies the necessary steps for the action to be performed:
“You are a marketer at ORGANIZATION_NAME.
The resort provides experiences guests can book throughout the day.
Write a marketing description for the experience below.
Make it sound unique and exciting.
Highlight the benefits of the experience.
The description should be between 80 and 100 words.”
Another few minutes were spent setting up the agent to automatically generate personalized emails to welcome guest for the next trip. Such email considers the client’s data, adds information from their event and services provided by the company, and can be written in a specific format.
For instance, to generate personalized welcoming guests email, it is necessary to provide detailed instructions in the prompt builder:
“Your name is SENDER_NAME. You work in the guest success team at ORGANIZATION_NAME, a luxury beachfront resort.
Generate an email welcoming the guest for their upcoming stay.
Guest name: GUEST_NAME.
Check-in date: NEXT_CHECK_IN_DATE.
Write a story that paints the picture of infinite possibilities at the resort and that weaves in some of the resort experiences that match the guest's interests.
List of resort experiences matching the guest's interests: EXPERIENCES.”
The majority of customization is accomplished through low-code automation. Utilizing Prompt Builder and Flow, an administrator can automate numerous workflows for themselves and their colleagues without the necessity of writing any code. So, if a business desires to modify the data that should be utilized, or the format for generating emails, for instance, it can be accomplished manually within a matter of minutes.
What if this is just a hype?
While the potential of artificial intelligence is widely discussed, it is crucial to acknowledge that this technology, comparable to other groundbreaking discoveries, must undergo a process of adaptation and awareness by humans. Frequently, the utilization of novel models, chatbots, and agents can yield unpredictable outcomes.
During the testing phase involving a substantial amount of data and assess the outcomes clients will receive, the analysis revealed that for the same set of parameters, the model could generate slightly different results. At this point, it’s difficult to determine whether the discrepancy that the model took into account of the parameters is something we’re not noticing or something else entirely.
However, the question arises:
Can a language model effectively learn from data that, due to variations in the formats of work between systems and humans, will likely be not ideal quality?
What will be the model’s response when a customer’s data record contains unverified information, inappropriate vocabulary, or other forms of erroneous content?
While exploring the details of the AgentForce implementation utilizing external sources, I came across an interesting formulation: “Customers can effortlessly extend the functionality of the platform using Flow, Mulesoft, and APEX.”
The origin of the term “easily” in this context remains unclear, but the presence of such an opportunity serves as a strong indicator of the organization’s focus on further scalability.
In December 2024, Salesforce announced the release of AgentForce 2.0. Based on the experience in creating the project using the initial version, it is pertinent to question whether this release was a fast response to competitive pressure and the prevailing trend, but not a result of careful and proven product improvement. After all, it is not feasible to say that Agentforce 1.0 is currently in a state of perfect functionality, and all users are universally satisfied with its performance.
Conclusion
AgentForce offers a range of capabilities that can significantly enhance your business operations:
* Personalized Email Generation: AgentForce can generate personalized emails based on customer data, adapting to the context and specific task requirements.
* Rapid and Flexible Information Search: It enables efficient and adaptable information retrieval from diverse sources and input formats.
* Create Field Generation template: automatically generate descriptions, ground the template using record merge fields.
Key Considerations:
* Limited Automation: AgentForce does not fully automate business processes without human intervention. While initial testing yields promising results, there is a risk of unforeseen errors or the inclusion of irrelevant data.
* Human Oversight: The generated results should be analyzed by a human expert with relevant business knowledge to ensure accuracy and completeness.
What is next?
The discussion on artificial intelligence is only at the very beginning of its evolutionary journey. Will the development of AI change the format of working with CRM systems? Definitely, and not only with them. Will AgentForce be a beneficiary of this change? Yes.
Salesforce’s solution is already being actively implemented and is gradually transforming the roles of agents and customers. The best thing you can do to understand the achievements of the trend and the caveats is to set up a simple agent, start using it in simple tasks and test the results. However, this should be done with conscious intent. The current level of technological advancement enables this solution to serve as a reasonably useful assistant, but human management should still be in place.